All Projects
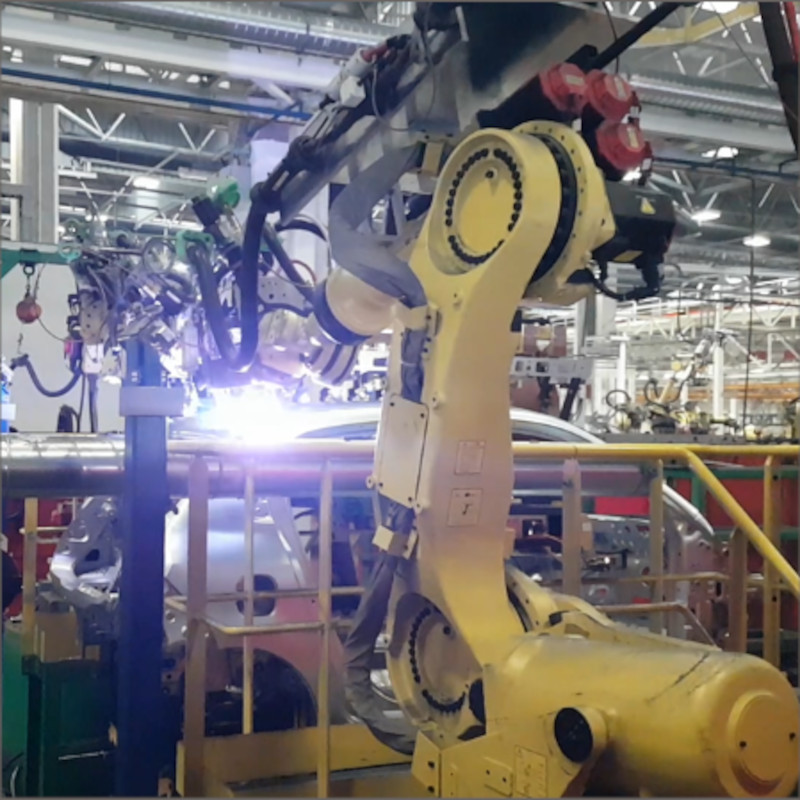
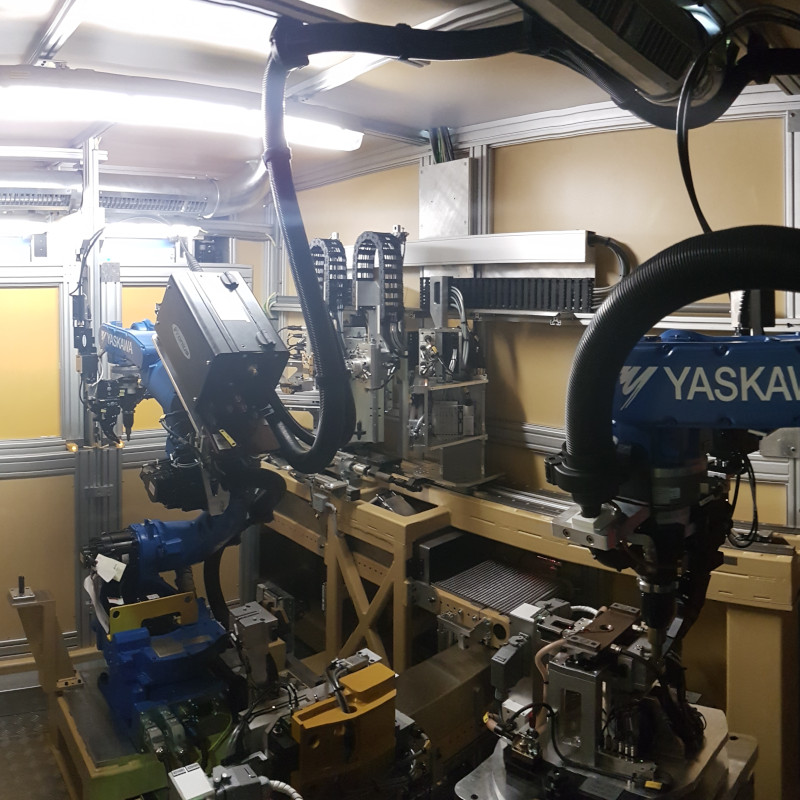
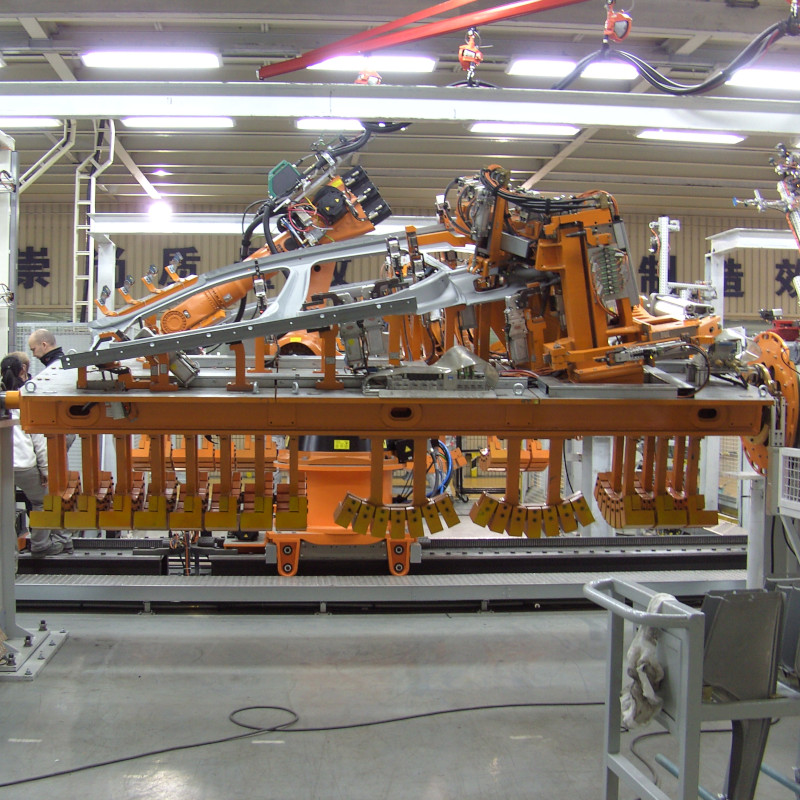
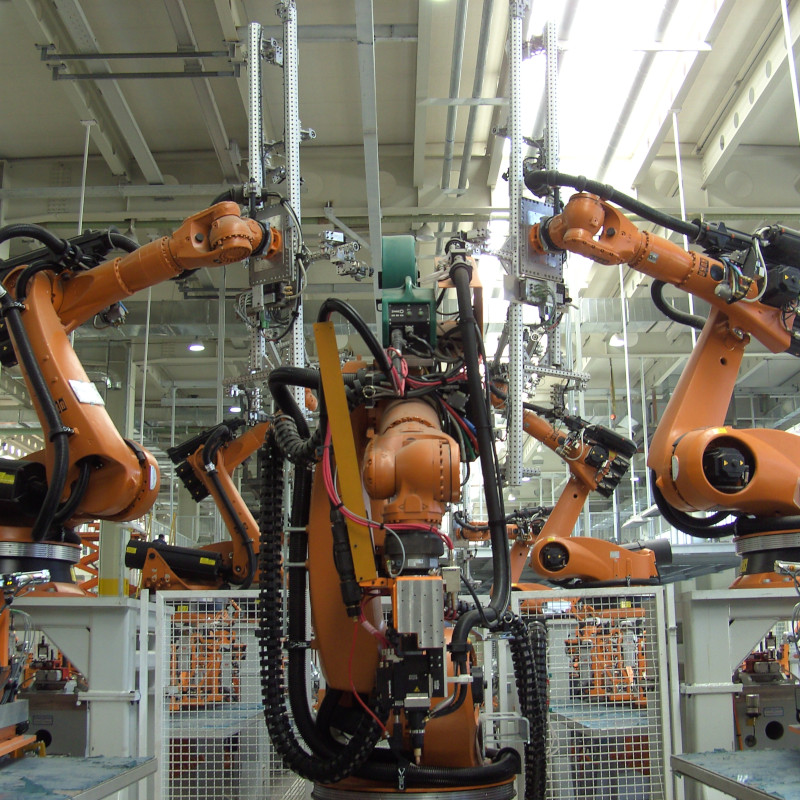
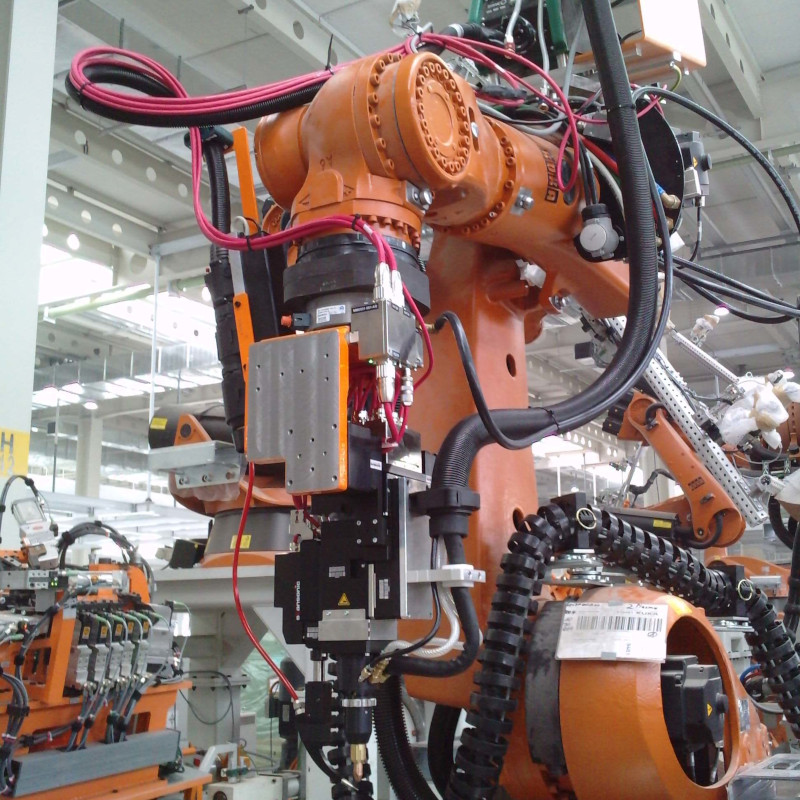
Roof seam brazing with Plasmatron
For a renowned European car manufacturer, Plasmatron was selected for the joint between the roof and the side panels. International projects, such as in France, Slovenia, Turkey or even Korea, were also undertaken here.
The galvanisation of the components proved to be a big challenge here. To compensate for the cathode wear due to the zinc vapour, an separate automatic cathode changing system (AKS) was developed for the Plasmatron. With this, it is possible to replace consumed cathodes within a few seconds in-line in an automated manner. Production and the cycle time are not influenced by the replacement process, as the replacement cycle takes place during parts handling. An operator only needs to intervene and insert a pre-equipped disc with new wear parts after 24 cycles.
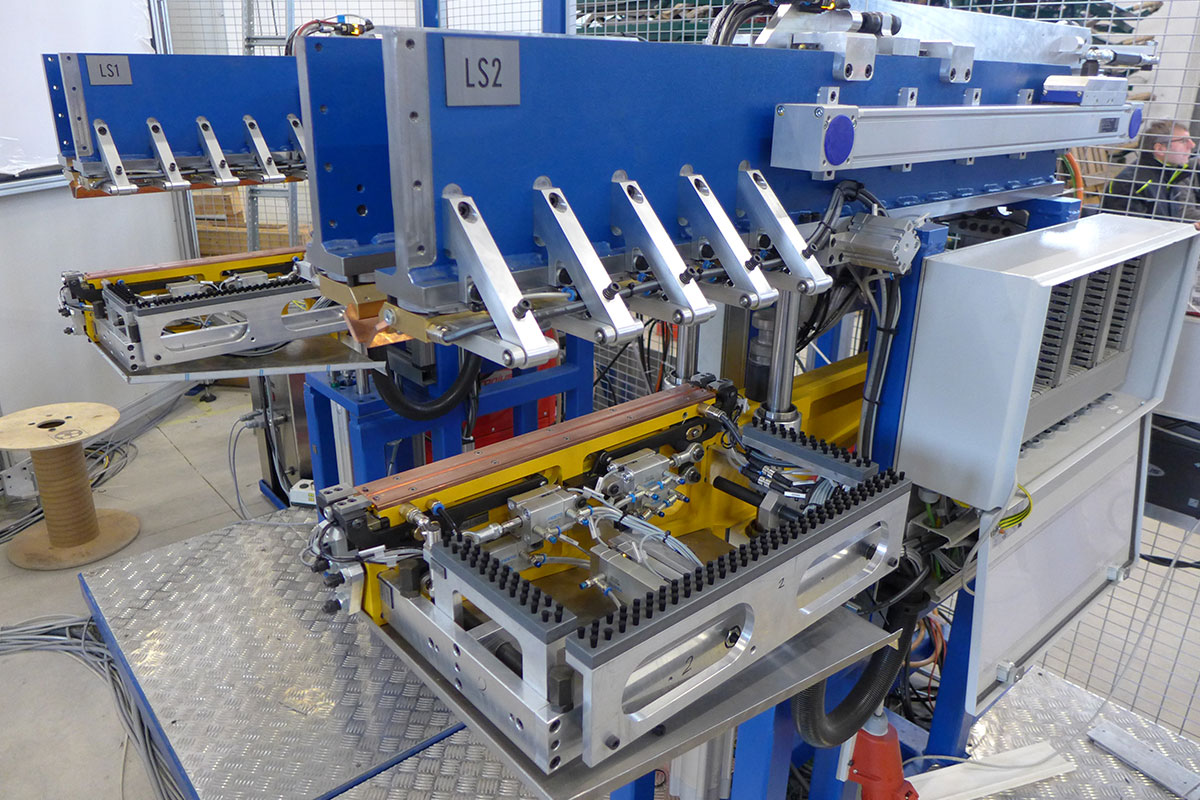
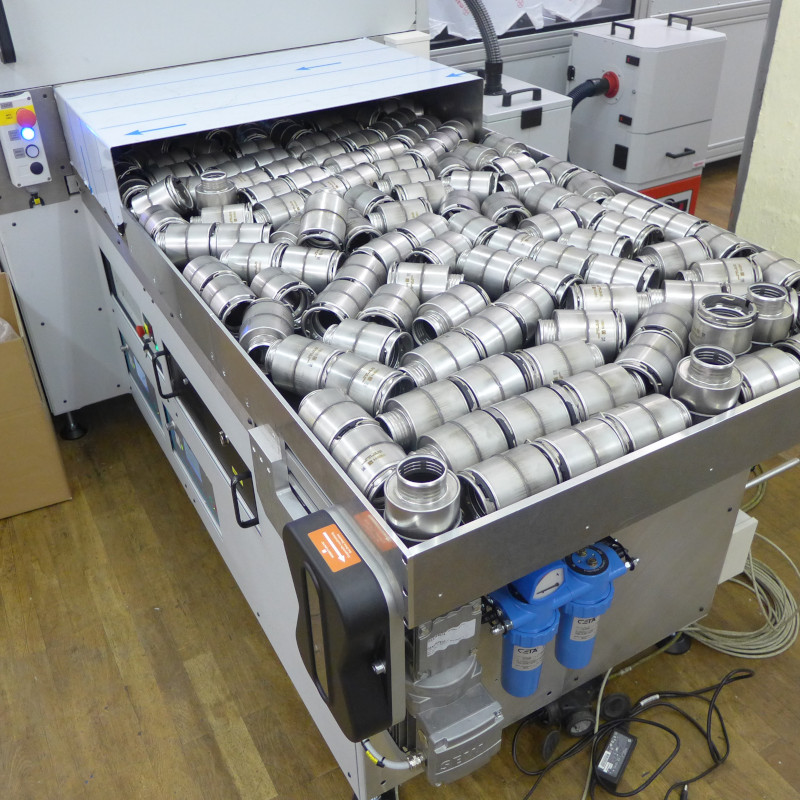
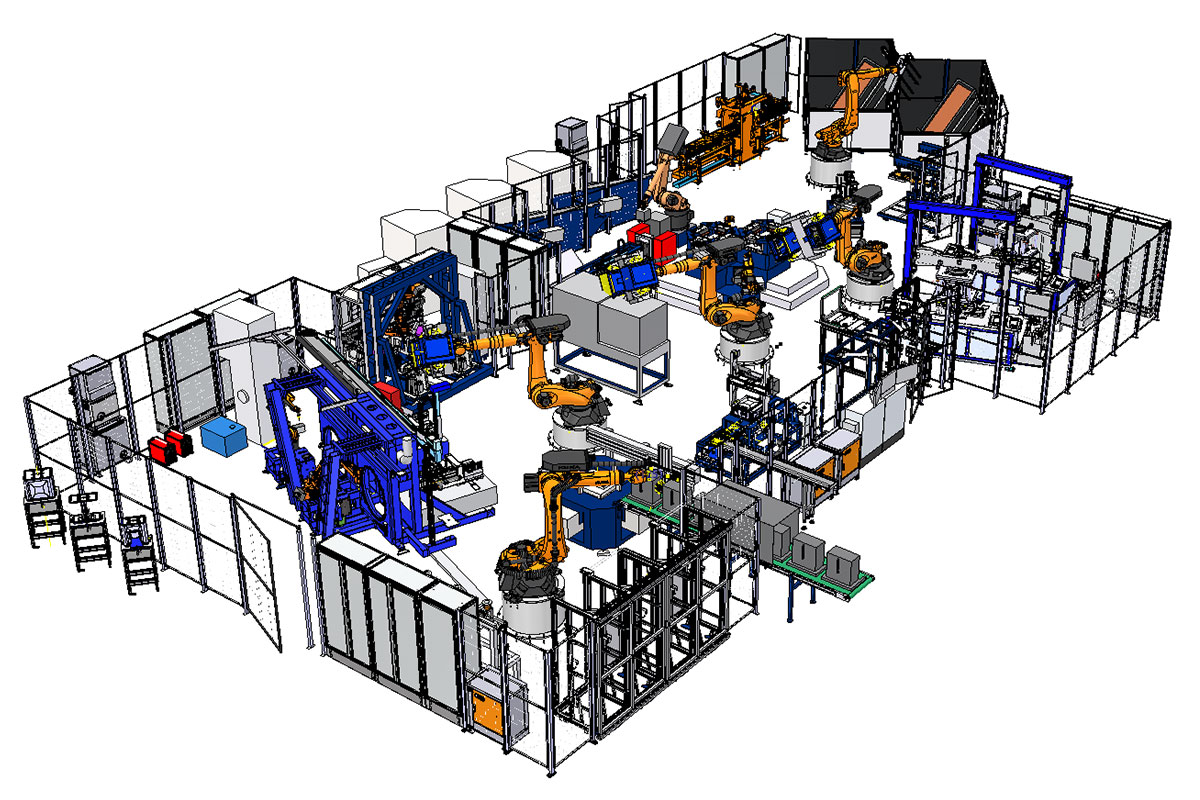
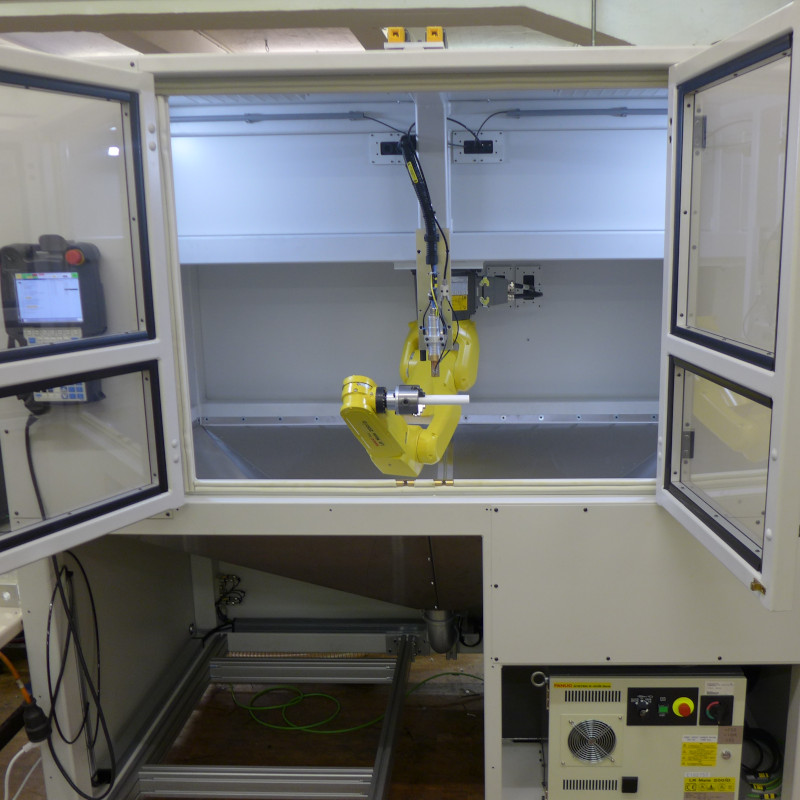
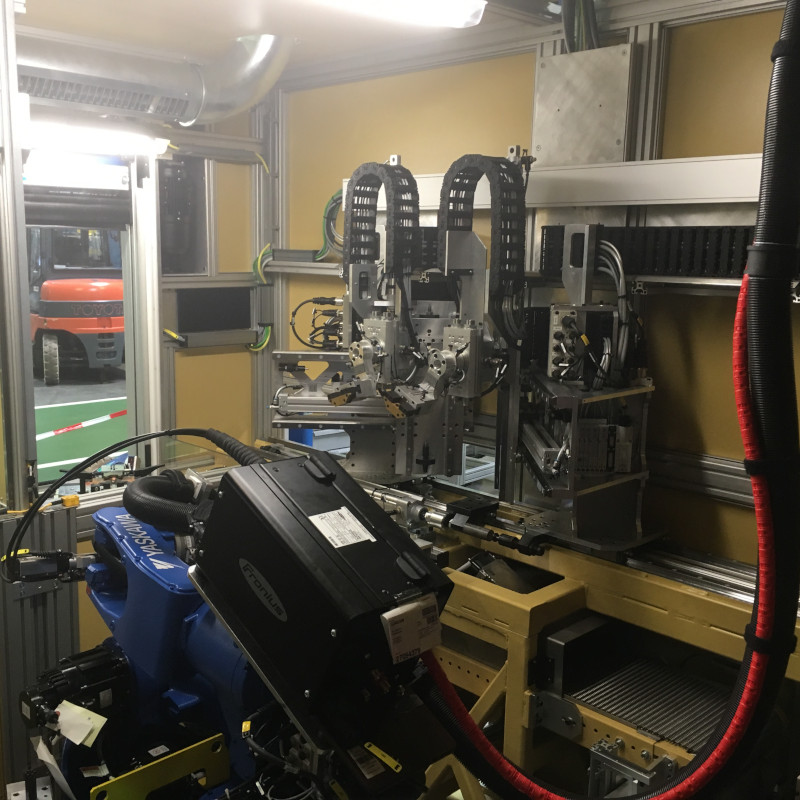
Cardan shaft welding machine (GWSA03)
The welded component is subsequently provided with a production code in a marking station and then placed into interim storage in a tower storage system. Once the cooling time has passed, the cardan shaft is transferred outwards on 2 different outlet conveyors for further processing.
A major challenge was the lot-size-1 productions for a model diversity consisting of several hundred different shafts. This target was achieved by automatic equipping of the welding adapters by means of handling robots.
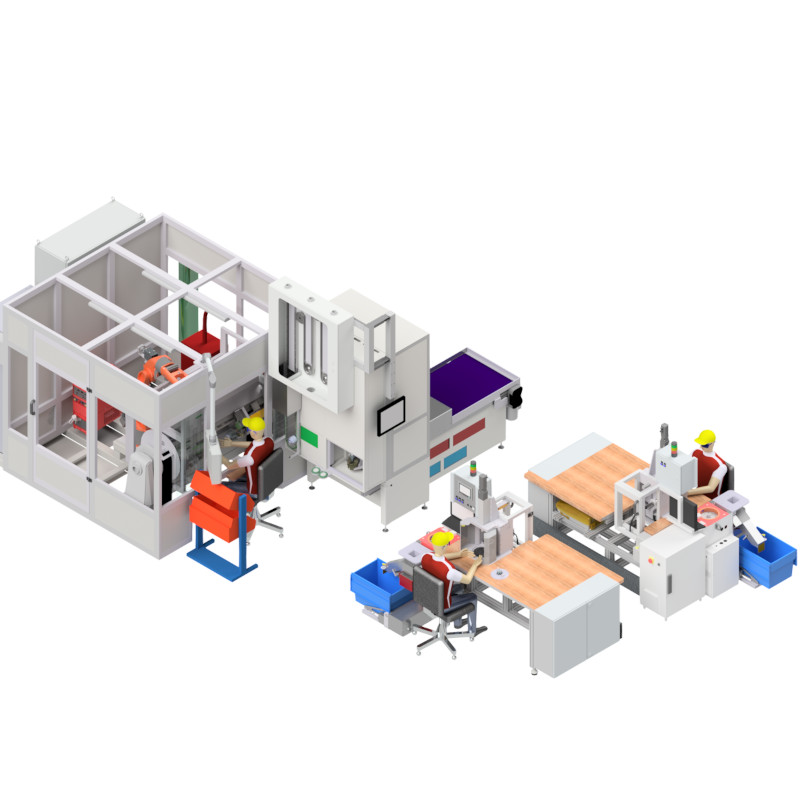
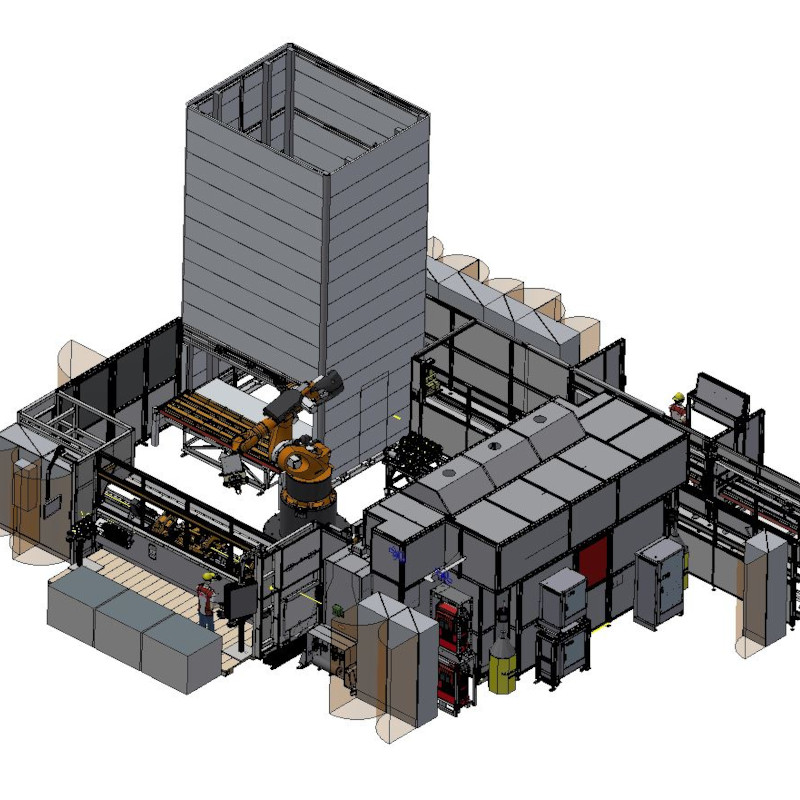
Steam oven production line
An entire production line was built for Miele, which manufactures the inner chamber of the steam oven starting from the metal blanks.
On an area of over 400 m², 11 robots work at 13 processing stations. This starts with the handover of the metal blanks, these are then shaped and further processed. Various welding tasks, such as linear welding the chamber, and welding of all add-on parts are performed using the Plasmatron process. All weld seams are checked by camera.
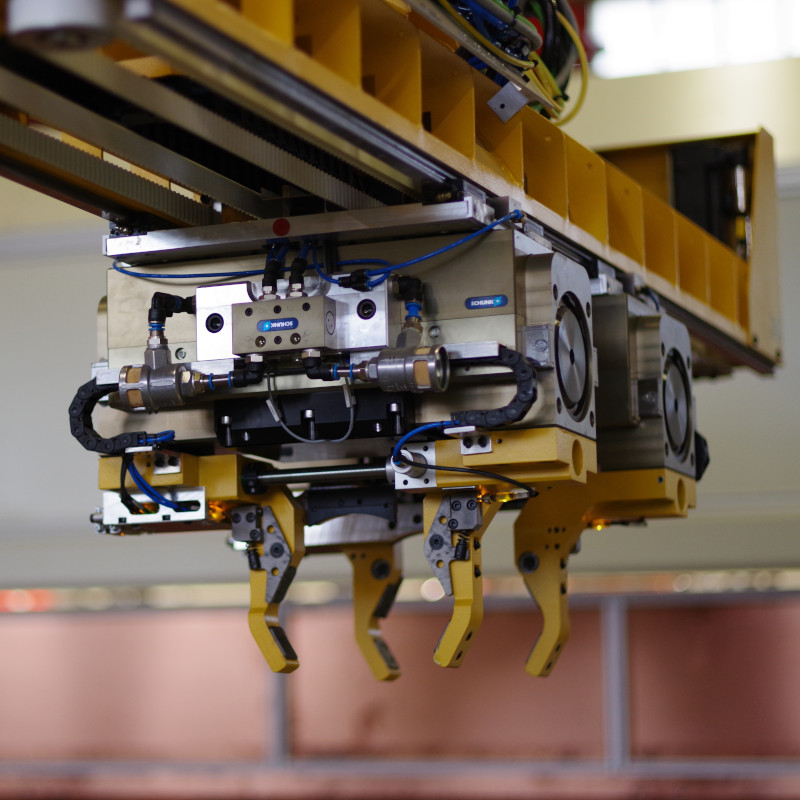
Additional processes such as bending, crimping and punching are performed on the production line. Thanks to functionally designed double grippers, the cooking chamber is handled completely automatically from the first to the last station on the production line.
3D plasma plotter
This coating system was built to coat components in 3D. For the coating process, the InoCoat or Micro Cold Plasma torch can be used.
The robot is mounted overhead in the cell and moves the component under the fixed coating torch.
Thanks to the 3-jaw chuck, individual adjustments can be implemented in a very simple manner for the different clamping options.
The powder is supplied by the Inofeed powder feeder.
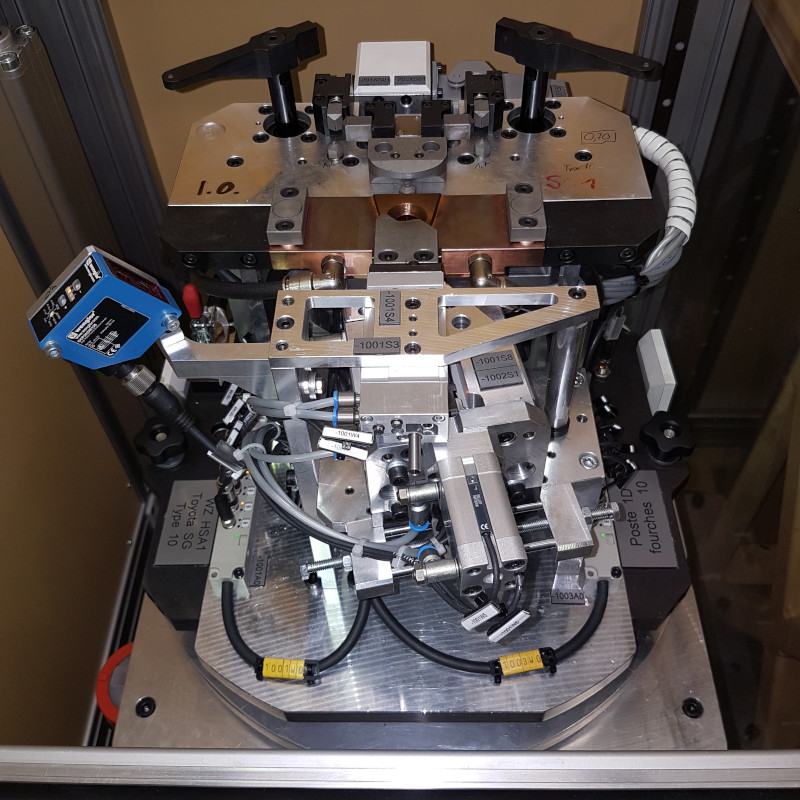
Fountain pen tip spot welding machine
This machine is used to weld ball tips onto the nibs of fountain pens. The system was designed at the request of the customer as a small-scale facility. The nibs are manually clamped in a fixture by the operator. After being clamped, the nib is moved into the system by means of a rotary table so that the ball tip can be added and then welded on. The ball tips are fed fully automatically from a magazine. The nib and ball tip are then aligned in the system and
precisely positioned to within +/-0.02 mm. The ball tip is then joined to the nib made from 24K gold by means of resistance welding. Due to the compactness of the plant, it is easy to move and can be used in a flexible manner.
R2R plasma plotter
The plasma plotter is a coating cell with which a wide range of tasks can be performed. The system is designed as a plug & play solution and can be used for complex research or even production tasks.
The InoCoat atmospheric plasma process is used for coating. The widest range of functional coats can thus also be produced on sensitive substrates. A changeover to the MCP Micro Cold Plasma torch is also possible as an option.
To be able to achieve very high movement speeds, the coating torch is positioned by means of an H-toothed belt drive.
On the customer’s premises, the system was then expanded by a system for winding up and unwinding films.
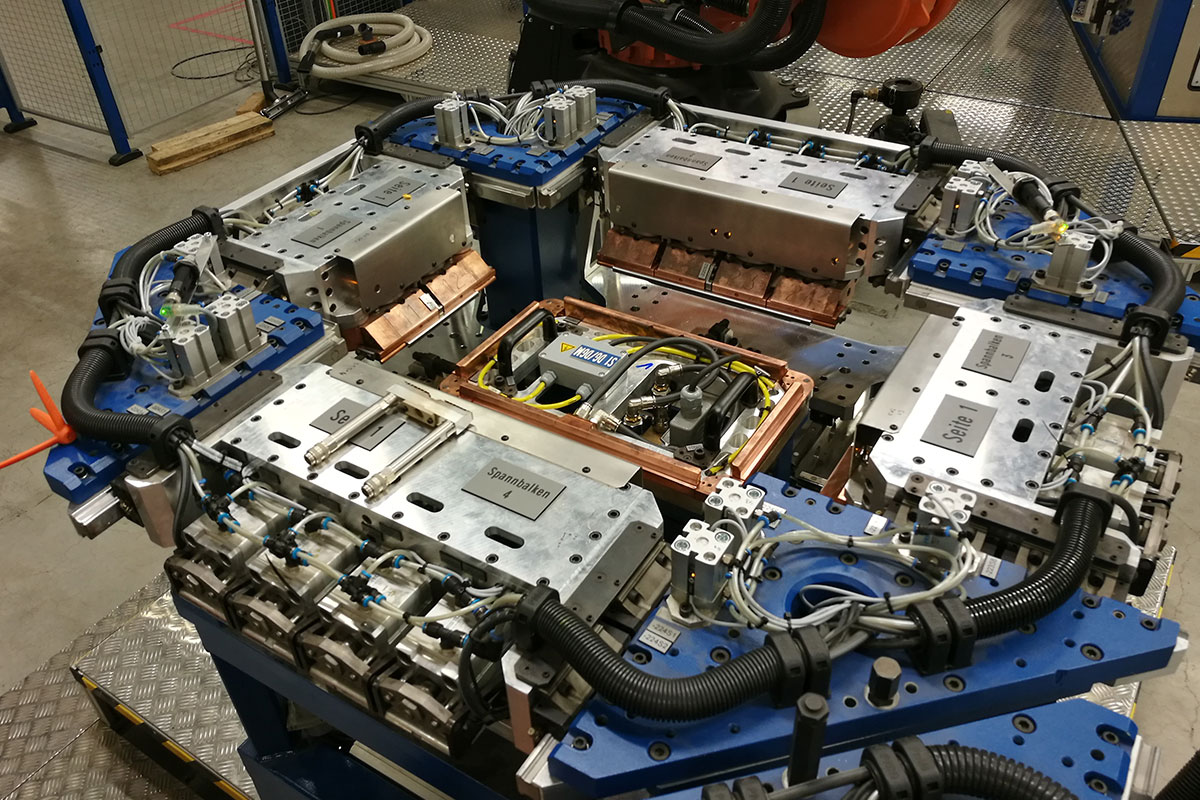
Shift fork welding machine
This compact welding machine was designed for welding shift forks on two lines. An operator inserts the shaft and fork into the welding device. They are then alternately welded and inserted at two stations. After the welding process, the component is moved to the next station for welding via transfer handling. So as not to damage the parts, a special heat-resistant plastic was used for the gripper jaws. After the second welding process, the part is removed and placed on a cooling belt, which transports the parts again to the operator’s side.
The material pairing was decisive for this machine. The shaft is made from heat-treated steel, while the fork is made from high-strength low-alloy steel. In addition, the components had to be welded without any weld spatters whatsoever. This task was solved in an outstanding manner with Plasmatron.
Due to the very small plant width specified by the customer, we had to develop a rather unconventional but functional machine concept in this case.
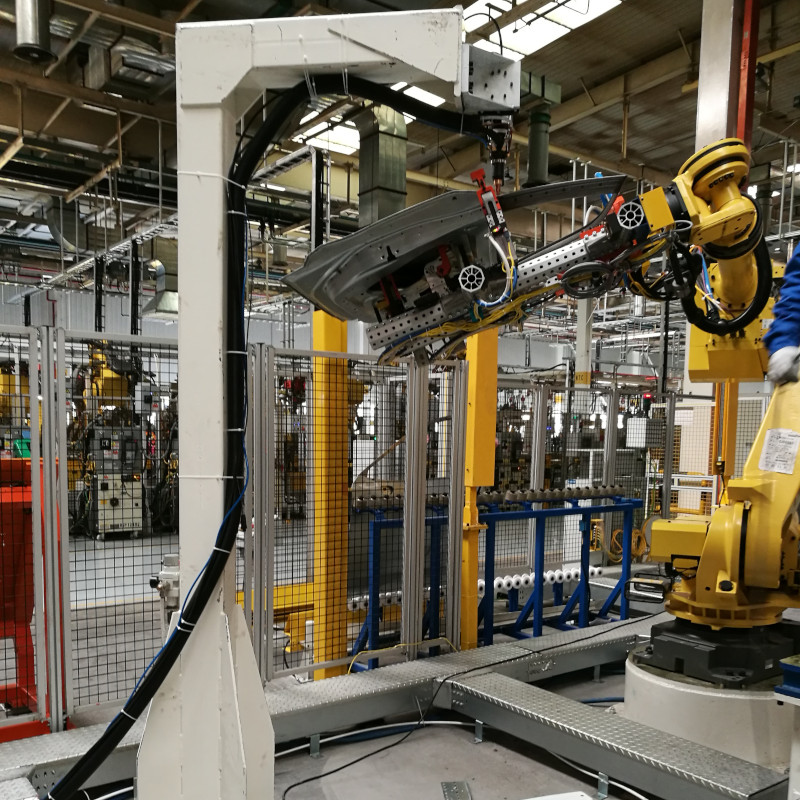
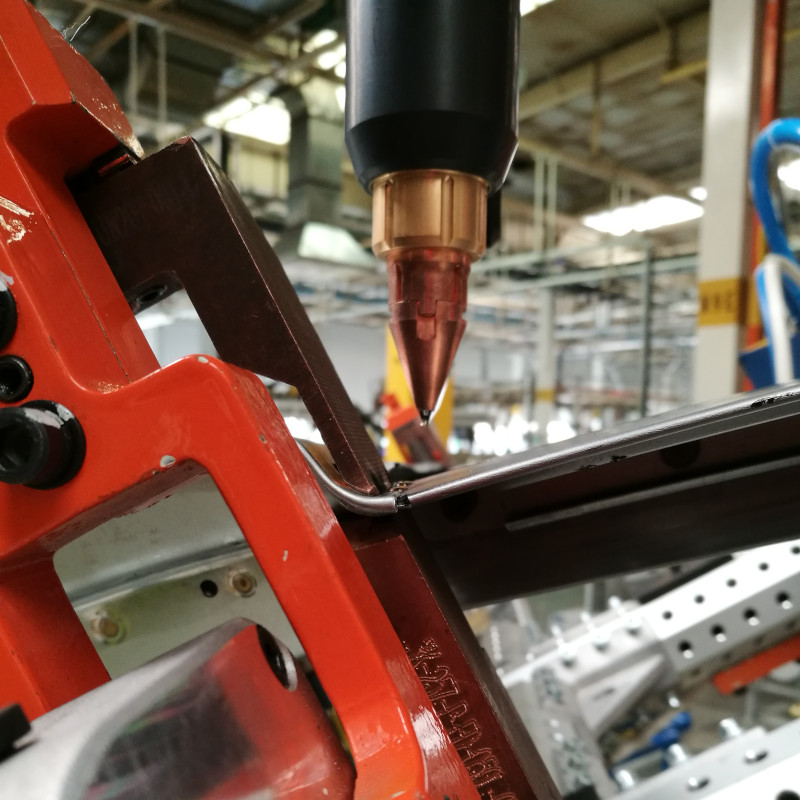
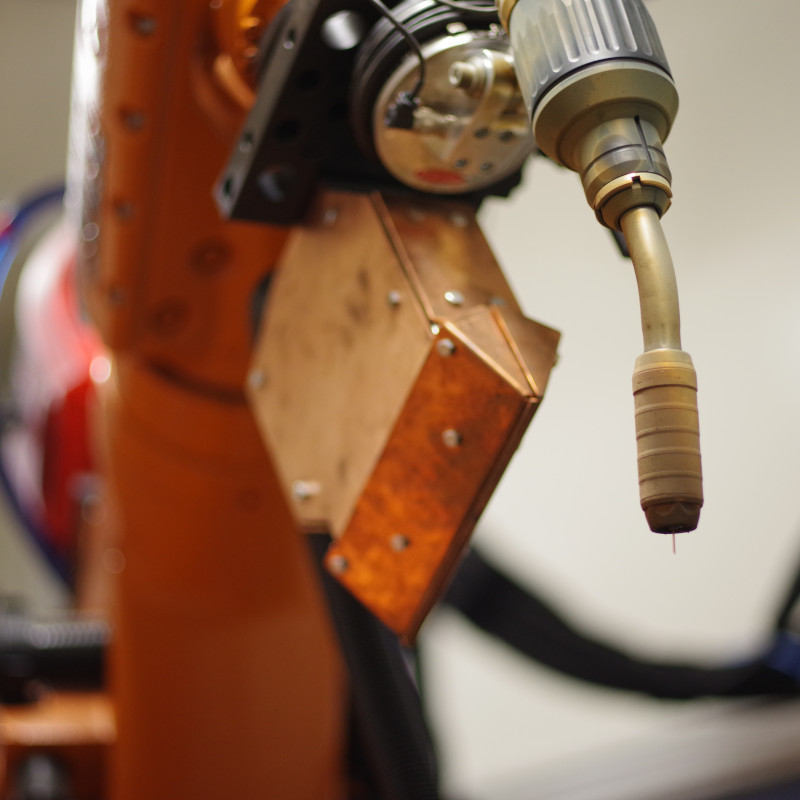
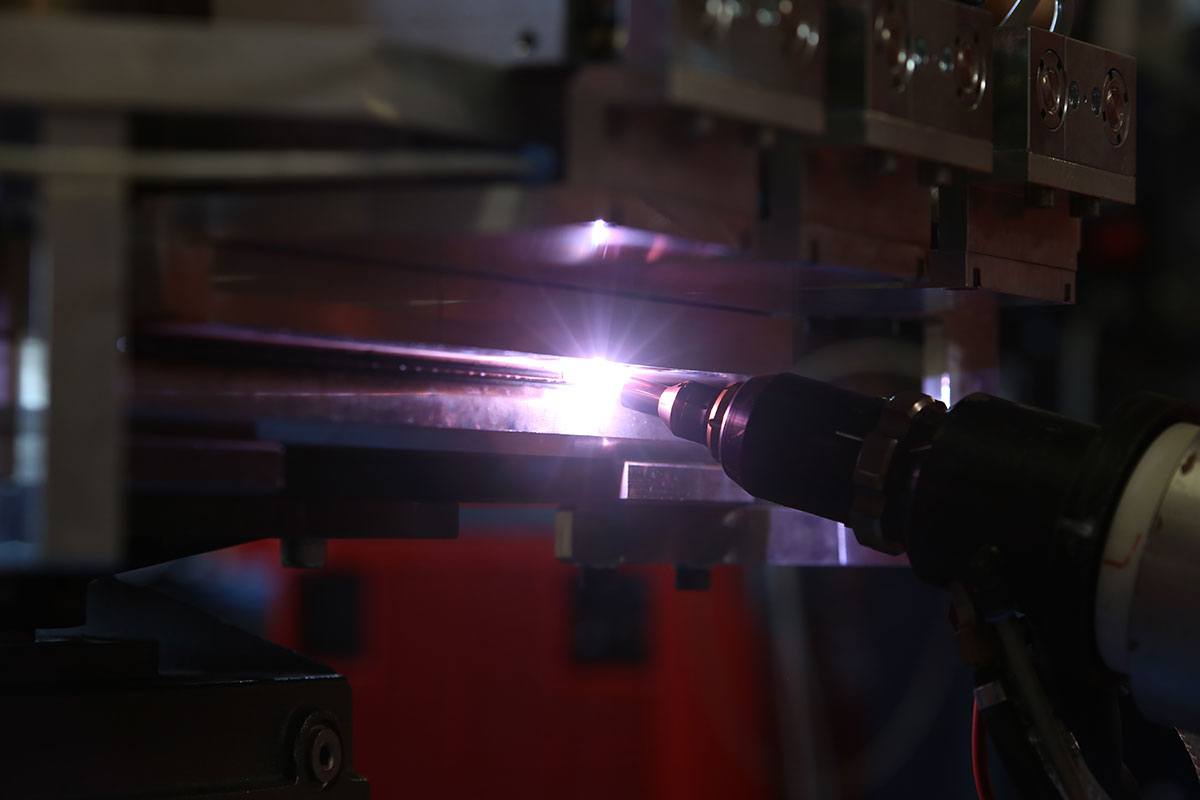
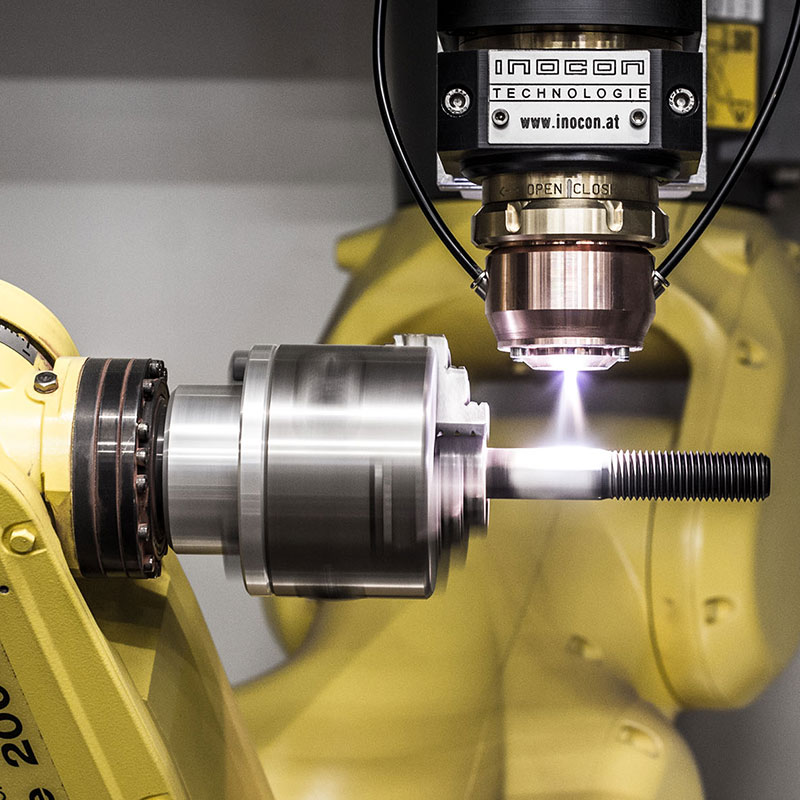
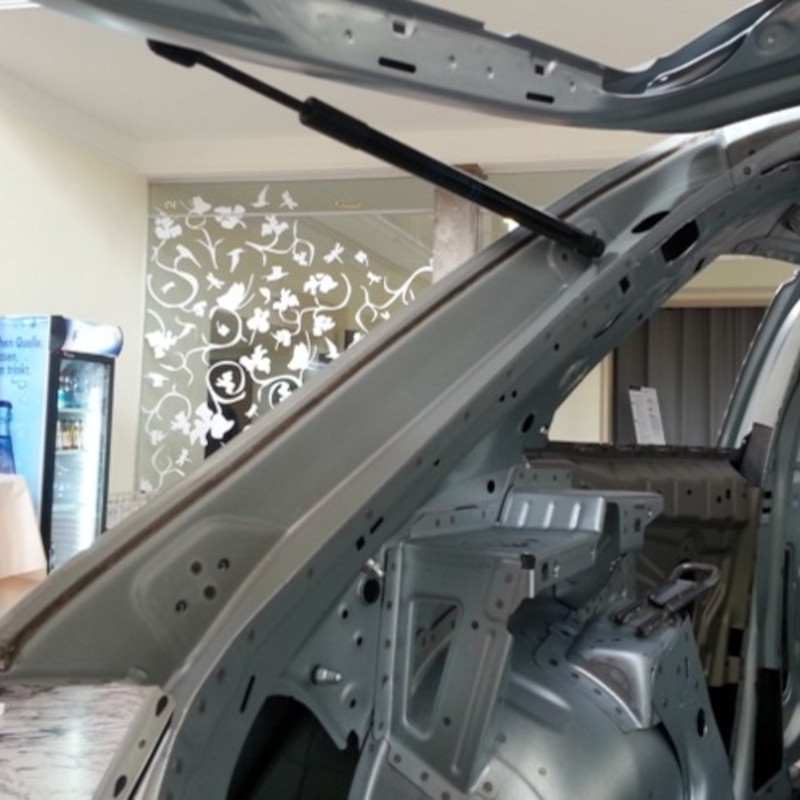
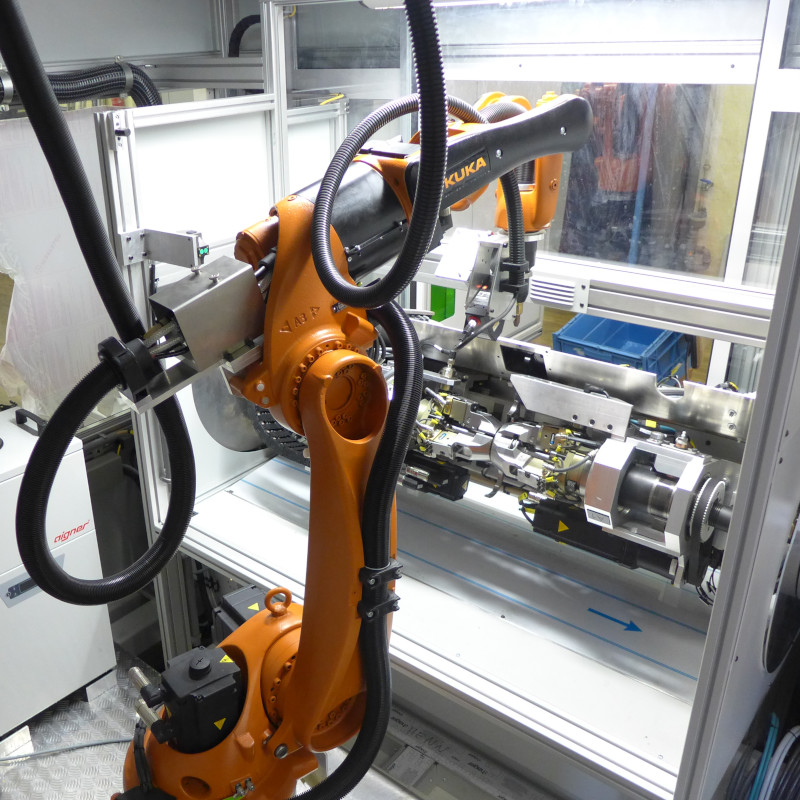
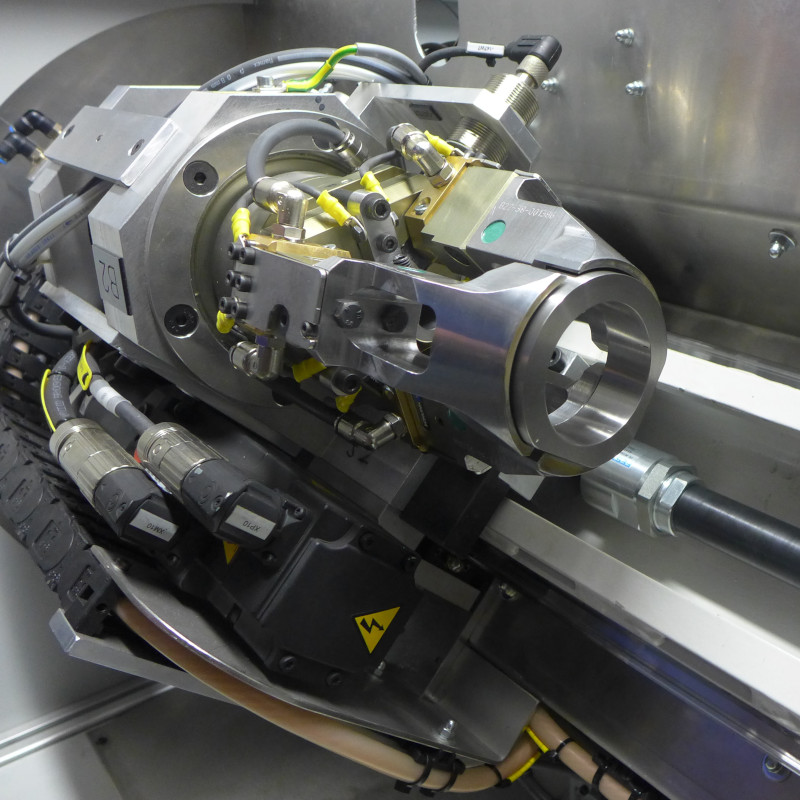
Plasmatron brazing of galvanised sheet metal
Plasmatron welding/brazing equipment is used at one of the German luxury car manufacturers in the area of the boot. Here the water drain (lap joint of galvanised sheet panels) is brazed using a CuSi3 additive.
The equipment consists of the Plasmatron welding technology, including power source and wire feeder, as well as additional components such as the tactile seam guidance, wire cutter and weld data monitoring.
The components have been commissioned by INOCON at a large number of locations in Europe, such as Germany, Spain, Hungary and Belgium, as well as internationally, for example in China and Brazil.
The Plasmatron guaranteed high quality standards and a production volume of approx. 600–700 body parts.
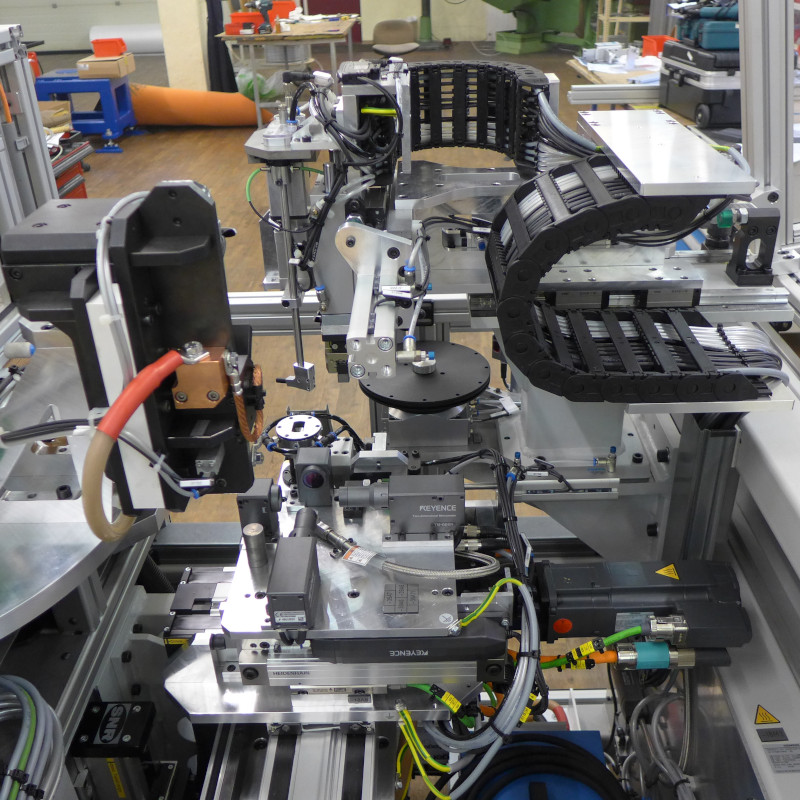
Resonator welding machine
The resonator welding machine welds together two deep-drawn parts made from stainless steel. An operator inserts both halves into insertion cavities, which are located on a turning device. This means the next device can be equipped during the welding process.
After clamping the component, the position of the weld seam is detected by a camera and the robot can be precisely positioned. Due to the low heat input during Plasmatron welding, the internal plastic parts are not damaged.
At two additional manual workstations, the internal plastic components were initially inserted as part of an upstream process and compression moulded at a monitored force.
After welding, a QR code is lasered onto the parts in order to guarantee traceability.
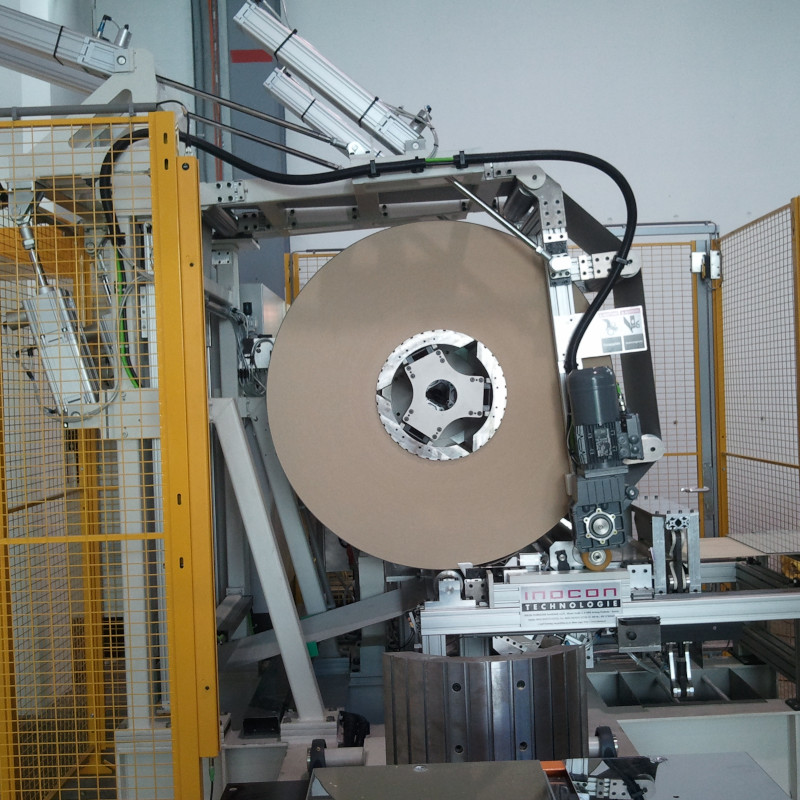
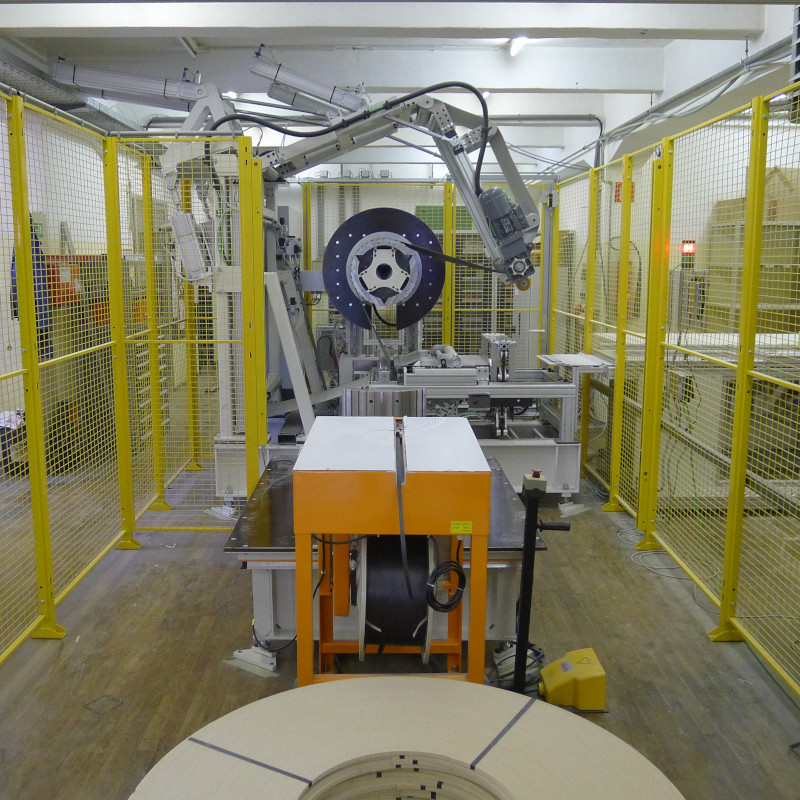
Batch winder
Something that was out of the ordinary for us as well was a batch winder for wooden press boards.
In this case, the boards were sawn to different widths using a multisaw. After the sawing, the segments are supplied to the winder and wound up by a rotary belt system. After the winding, the entire stack is pushed onto a setdown table and rotated through 90°. There, a robot picks up the individual segments.
If this appeals to you, send us your application and become part of our team.